Lybic platform placeholder - comprehensive AI platform for building and deploying intelligent agents
Lybic GUI Agent is an open-source framework that enables developers and businesses to create intelligent computer-use agents,mobile-use agents, and intelligent agents that can understand and interact with graphical user interfaces across Windows, macOS, Linux and Android(via lybic Android Sandbox) platforms.
Skip the setup? Try Lybic GUI Agent in our Playground with a few clicks.(Only in the Chinese mainland supported)
- 2025/10/17: We have completed the verification test of the 100-step task at OS-world.
- 2025/09/14: The paper has been accepted by arxiv
- 2025/09/09: We achieved the world's first place in the 50-step length of OS-world!
- 2025/08/08: Released v0.1.0 of Lybic GUI Agent library, with support for Windows, Mac, Ubuntu and Lybic API!
- Multiple LLMs providers: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, xAI , AzureOpenAI, DeepSeek, Qwen, Doubao, ZhipuGLM
- Aggregation Model Provider: Bedrock, Groq, Monica, OpenRouter, SiliconFlow
- RAG: We support RAG, and this capability is provided as an extension
- Cross-Platform GUI Control: Windows, Linux, macOS, Android Supported
- Observability: Supported
- Local Deployment: Supported
- Cloud Sandbox Environment: Supported
🎉 Agents Online Demo
🎯 Current Results
| Benchmark | Lybic GUI Agent | Previous SOTA |
|---|---|---|
| OSWorld Verified (50 step) | 57.1% | 54.2% |
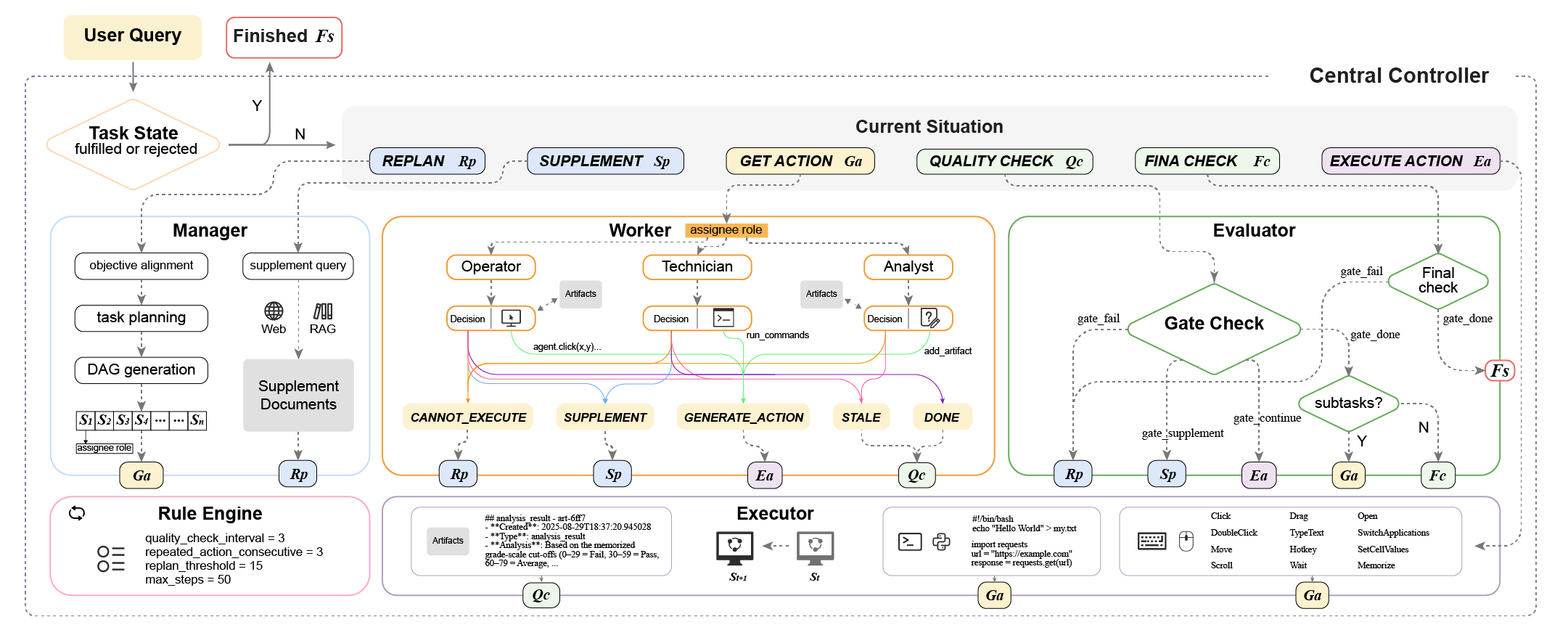
Fig. Lybic GUI Agent system structure
Warning
To leverage the full potential of Lybic GUI Agent, we support multiple model providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, and Doubao. For the best visual grounding performance, we recommend using UI-TARS models.
You can install Lybic GUI Agent by using pip:
pip install lybic-guiagentsNote for Windows Users: If you encounter Unicode decoding errors during installation (especially on systems with non-UTF-8 default encoding like Chinese Windows), set the following environment variable before running pip:
set PYTHONUTF8=1Then run the installation command again. This enables Python's UTF-8 mode, which resolves encoding issues on Windows.
You can use UV (a modern Python package manager) version 0.8.5 for installation:
# 1. Install UV if not already installed
# macOS and Linux
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/0.8.5/install.sh | sh
# Windows
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/0.8.5/install.ps1 | iex"
# testing uv installation, version should be 0.8.5
uv --version
# 2. Install the python 3.14
uv python install 3.14
# 3. Create a virtual environment
uv venv -p 3.14
# 4. Activate the virtual environment
# macOS and Linux
source .venv/bin/activate
# Windows
.venv\Scripts\activate
# 5. Install dependencies (using locked versions)
uv sync
# 6. Install the package locally in development mode
uv pip install -e .Note for Windows Users: If you encounter Unicode decoding errors during dependency installation (e.g.,
UnicodeDecodeError: 'gbk' codec can't decode byte), this is typically caused by packages with non-UTF-8 encoded files. Set this environment variable before runninguv sync:set PYTHONUTF8=1This enables Python's UTF-8 mode, which resolves encoding issues on Windows systems with non-UTF-8 default locales.
The simplest way to configure API keys is to:
- Copy
gui_agents/.env.exampletogui_agents/.env - Edit the
.envfile and add your API keys
We provide two pre-configured tool settings:
tools_config_en.json: Configured for English language models (Gemini, Exa)tools_config_cn.json: Configured for Chinese language models (Doubao, bocha)
The agent uses tools_config.json by default. You can:
- Copy either
tools_config_en.jsonortools_config_cn.jsontotools_config.json - Or create your own custom configuration
If you are using tools_config_cn.json and use pyautogui backend, the environment variable only ARK_API_KEY should be set.
If you are using tools_config_en.json and use pyautogui backend, you should set those 3 environment variables:
GEMINI_ENDPOINT_URL=https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/
GEMINI_API_KEY=your_gemini_api_key
ARK_API_KEY=your_ark_api_key# For English models
cp gui_agents/tools/tools_config_en.json gui_agents/tools/tools_config.json
# For Chinese models
cp gui_agents/tools/tools_config_cn.json gui_agents/tools/tools_config.jsonNote: Our recommended configuration uses
doubao-1-5-ui-tars-250428for"tool_name": "grounding" or "fast_action_generator"andclaude-sonnet-4-20250514ordoubao-seed-1-6-250615for other tools such as"tool_name": "action_generator". You can customize the model configuration in the tools configuration files. Do not modify the"tool_name"intools_config.jsonfile. To change the"provider"and"model_name"intools_config.jsonfile, see model.md
Run Lybic GUI Agent with python in the command-line interface:
python gui_agents/cli_app.py [OPTIONS]This will show a user query prompt where you can enter your instructions and interact with the agent.
-
--backend [lybic|lybic_mobile|pyautogui|pyautogui_vmware]: Specifies the backend to use for controlling the GUI. Defaults tolybic. -
--query "YOUR_QUERY": Optional, can be input during the runtime; if provided, the agent will execute the query and then exit. -
--max-steps NUMBER: Sets the maximum number of steps the agent can take. Defaults to50. -
--mode [normal|fast]: (Optional) Selects the agent mode.normalruns the full agent with detailed reasoning and memory, whilefastmode executes actions more quickly with less reasoning overhead. Defaults tonormal. -
--enable-takeover: (Optional) Enables user takeover functionality, allowing the agent to pause and request user intervention when needed. By default, user takeover is disabled. -
--disable-search: (Optional) Disables web search functionality. By default, web search is enabled.
Run in interactive mode with the lybic backend:
python gui_agents/cli_app.py --backend lybicRun a single query with the pyautogui backend and a maximum of 20 steps:
python gui_agents/cli_app.py --backend pyautogui --query "Find the result of 8 × 7 on a calculator" --max-steps 20Run in fast mode with the pyautogui backend:
python gui_agents/cli_app.py --backend pyautogui --mode fastWarning
The agent will directly control your computer with --backend pyautogui. Please use with care.
You can also run Lybic GUI Agent using Docker. This is an example of how to run it with the lybic backend:
docker run --rm -it --env-file gui_agents/.env agenticlybic/guiagent --backend lybicNote: This command starts the agent in interactive mode. The
--env-fileflag points to the environment file. Please ensure the path is correct.
The simplest way to configure Lybic Sandbox is still to edit the .env file and add your API keys, as mentioned in the API Key Configuration section.
LYBIC_API_KEY=your_lybic_api_key
LYBIC_ORG_ID=your_lybic_org_id
LYBIC_MAX_LIFE_SECONDS=3600Note: If you want to use a precreated Lybic Sandbox in Lybic Dashboard, you need to set the
LYBIC_PRECREATE_SIDto the precreated Sandbox ID.
LYBIC_PRECREATE_SID=SBX-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
You can interact with the agent programmatically either by importing it as a Python library or by running it as a gRPC service.
After installing lybic-guiagents, you can import and use its components directly in your Python code.
Main Components:
AgentService: High-level service interface (recommended for most users).AgentS2,AgentSFast: Core agent implementations.HardwareInterface: Hardware abstraction layer for controlling the GUI.ServiceConfig: Configuration management.
Quick Start:
from gui_agents import AgentService
service = AgentService()
result = service.execute_task("Take a screenshot")
print(f"Task completed: {result.status}")You can also run the agent as a standalone gRPC service, which is ideal for distributed architectures or integrating with applications written in other languages.
1. Running the gRPC Server
First, run the gRPC server using Docker. This command overrides the default CLI entrypoint and starts the gRPC service on port 50051.
docker run --rm -it -p 50051:50051 --env-file gui_agents/.env agenticlybic/guiagent /app/.venv/bin/lybic-guiagent-grpcNote: The
-p 50051:50051flag maps the container's gRPC port to your host machine.
Alternative: Running the RESTful API Server
You can also run the RESTful API server for HTTP/REST access:
docker run --rm -it -p 8080:8080 --env-file gui_agents/.env agenticlybic/guiagent /app/.venv/bin/lybic-guiagent-restfulThe RESTful API provides similar functionality to the gRPC server but uses HTTP/REST protocol with Server-Sent Events (SSE) for streaming. Access the interactive API documentation at http://localhost:8080/docs. See docs/restful_api.md for detailed usage guide.
Optional: Enable Prometheus Monitoring
The gRPC service supports optional Prometheus metrics for monitoring task execution, resource usage, and performance. To enable:
# Install Prometheus dependencies
pip install -e ".[prometheus]"
# Run with Prometheus enabled
docker run --rm -it \
-p 50051:50051 \
-p 8000:8000 \
-e ENABLE_PROMETHEUS=true \
-e PROMETHEUS_PORT=8000 \
--env-file gui_agents/.env \
agenticlybic/guiagent /app/.venv/bin/lybic-guiagent-grpcAccess metrics at http://localhost:8000/metrics. See Prometheus Metrics Documentation for details.
2. Python Client Example
Once the service is running, you can interact with it using a gRPC client. Here is a Python example of how to send an instruction to the agent and stream its progress.
First, ensure you have the necessary gRPC libraries and generated protobuf stubs:
# Install gRPC tools
pip install grpcio grpcio-tools
# Generate stubs from the .proto file
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -Igui_agents/proto --python_out=gui_agents/proto/pb --grpc_python_out=gui_agents/proto/pb --pyi_out=gui_agents/proto/pb gui_agents/proto/agent.protoThen, you can use the following script to communicate with the agent:
import asyncio
import grpc
from gui_agents.proto.pb import agent_pb2, agent_pb2_grpc
async def run_agent_instruction():
# Connect to the gRPC server
async with grpc.aio.insecure_channel('localhost:50051') as channel:
# Create a stub for the Agent service
stub = agent_pb2_grpc.AgentStub(channel)
# Create a request to run an instruction
request = agent_pb2.RunAgentInstructionRequest(
instruction="Open a calculator and compute 1 + 1"
)
print(f"Sending instruction: '{request.instruction}'")
# Call the RunAgentInstruction RPC and iterate over the stream of responses
try:
async for response in stub.RunAgentInstruction(request):
print(f"[{response.stage}] {response.message}")
except grpc.aio.AioRpcError as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e.details()}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(run_agent_instruction())The gRPC service supports persistent storage for task status and history using PostgreSQL. This allows task data to survive service restarts.
- Default Behavior: By default, tasks are stored in memory and will be lost when the service stops.
- Enable Persistence: To enable PostgreSQL persistence, you need to:
- Install the required dependency:
- If installing from PyPI:
pip install lybic-guiagents[postgres] - If installing from source:
uv pip install .[postgres]
- If installing from PyPI:
- Set the following environment variables:
# Use the postgres backend instead of the default 'memory' TASK_STORAGE_BACKEND=postgres # Set your PostgreSQL connection string POSTGRES_CONNECTION_STRING=postgresql://user:password@host:port/database
- Install the required dependency:
- Docker Usage: The
agenticlybic/guiagentDocker image comes with PostgreSQL support pre-installed. You only need to set the environment variables above to enable persistence when running the gRPC service container.
To use PyAutoGUI with VMware, you need to install VMware Workstation Pro (on Windows) and create a virtual machine.
Next, you need to download the Windows-x86.zip and Ubuntu-x86.zip from Hugging Face. Then unzip them into ./vmware_vm_data/Windows-x86 and ./vmware_vm_data/Ubuntu-x86 directory.
Finally, you need to edit the .env file and set the USE_PRECREATE_VM environment variable to the name of the virtual machine. USE_PRECREATE_VM support Windows and Ubuntu on x86 arch computer.
USE_PRECREATE_VM=UbuntuProblem: KeyError or authentication errors when running the agent.
Solution:
- Ensure your
.envfile is properly configured with valid API keys - Check that environment variables are set correctly:
# For English models export GEMINI_API_KEY=your_gemini_api_key export ARK_API_KEY=your_ark_api_key # For Chinese models export ARK_API_KEY=your_ark_api_key
- Verify API key permissions and quotas
Problem: ModuleNotFoundError or package import errors.
Solution:
- Ensure you're using Python >= 3.12
- Activate the virtual environment:
# macOS/Linux source .venv/bin/activate # Windows .venv\Scripts\activate
- Reinstall dependencies:
uv sync uv pip install -e . # uv pip install -e . -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
Problem: UnicodeDecodeError during package installation on Windows, especially with error messages like:
UnicodeDecodeError: 'gbk' codec can't decode byte 0xa2 in position 905: illegal multibyte sequence
Solution:
This issue occurs when Python tries to read package metadata files using the system's default encoding (e.g., GBK on Chinese Windows) instead of UTF-8. To resolve this:
Option 1: Set environment variable temporarily (Command Prompt)
set PYTHONUTF8=1
pip install lybic-guiagentsOption 2: Set environment variable temporarily (PowerShell)
$env:PYTHONUTF8=1
pip install lybic-guiagentsOption 3: Set environment variable permanently (System-wide)
- Open System Properties → Advanced → Environment Variables
- Add new system variable:
- Variable name:
PYTHONUTF8, Value:1
- Variable name:
- Restart your terminal and try installation again
Option 4: Use Python 3.15+ (Future) Python 3.15+ will enable UTF-8 mode by default on Windows (PEP 686), which will eliminate this issue.
Note: Some users have reported success with additionally setting
PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8, thoughPYTHONUTF8=1should be sufficient in most cases. If you still encounter issues after settingPYTHONUTF8=1, try addingset PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8in Command Prompt (or$env:PYTHONIOENCODING="utf-8"in PowerShell).
Problem: Connection timeout or Sandbox creation failed.
Solution:
- Check network connectivity to Lybic servers
- Verify
LYBIC_ORG_IDandLYBIC_API_KEYare correct - Ensure sufficient quota in your Lybic account
- Try increasing
LYBIC_MAX_LIFE_SECONDSif sandbox times out
Problem: Virtual machine fails to start or control.
Solution:
- Ensure VMware Workstation Pro is properly installed
- Check that VM files are extracted to correct directories:
./vmware_vm_data/Windows-x86/./vmware_vm_data/Ubuntu-x86/
- Verify VMware service is running
- Set correct
USE_PRECREATE_VMenvironment variable
Problem: Slow response times or poor grounding accuracy.
Solution:
- Use recommended models for better performance:
- Visual grounding:
doubao-1-5-ui-tars-250428 - Action generation:
claude-sonnet-4-20250514
- Visual grounding:
- Switch to
--mode fastfor quicker execution - Reduce
--max-stepsfor shorter tasks
If you encounter issues not covered here:
- Check the GitHub Issues for similar problems
- Review the Lybic Documentation
- Create a new issue with:
- Your operating system and version
- Python version and environment details
- Complete error messages
- Steps to reproduce the issue
If you find this codebase useful, please cite:
@misc{guo2025agenticlybicmultiagentexecution,
title={Agentic Lybic: Multi-Agent Execution System with Tiered Reasoning and Orchestration},
author={Liangxuan Guo and Bin Zhu and Qingqian Tao and Kangning Liu and Xun Zhao and Xianzhe Qin and Jin Gao and Guangfu Hao},
year={2025},
eprint={2509.11067},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.11067},
}This project is distributed under Apache 2.0 License. Therefore, you can modify the source code and release it commercially.